Tunable Passively Q-Switched and Mode-Locked Fiber Laser at 1.9 µm Region Using a
Mixture of Gold Nanorods and Polyvinyl Alcohol as a Saturable Absorber
Scientists from the Lakehead University have demonstrated the use of Nanopartz Gold Nanorods as a saturable absorber in a q-switched and mode locked fiber laser.
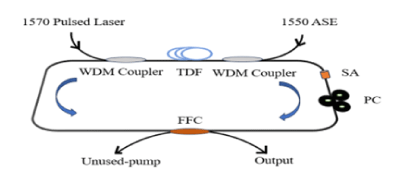
Schematic of the experimental setup to produce tunable laser at 1.9 µm band |
Overview
This study explores the development of a tunable passively Q-switched and mode-locked fiber laser operating in the 1.9 μm region, achieved using a novel saturable absorber (SA) composed of gold nanorods (GNRs) embedded in polyvinyl alcohol (PVA). This wavelength region is particularly important for applications in medical diagnostics, environmental sensing, and LIDAR systems. By leveraging the nonlinear optical properties of GNRs, this work presents a highly efficient and tunable laser system that offers a cost-effective and robust alternative to conventional fiber lasers. Our target audience includes laser physicists, photonics researchers, and professionals in the biomedical and remote sensing fields.
Problem Addressed
Fiber lasers in the 1.9 μm spectral range have significant demand due to their applications in non-invasive medical imaging, eye-safe LIDAR systems, and atmospheric gas detection. However, current solutions suffer from limitations such as high cost, complexity, and inefficiencies in passive Q-switching and mode-locking mechanisms. Conventional SAs, like semiconductor-based absorbers, often face performance degradation and operational constraints. Thus, an effective, stable, and tunable alternative is needed to enhance the capabilities of fiber lasers in this spectral range.
TEM image of Nanopartz GNRs with aspect ratio 20 in PVA solution |
Solution
Our research presents a tunable passively Q-switched and mode-locked fiber laser system using a composite SA made of GNRs embedded in PVA. Gold nanorods exhibit strong surface plasmon resonance (SPR) in the near-infrared region, enabling effective nonlinear absorption for stable and tunable laser operation. By incorporating the GNR-PVA SA into the fiber laser cavity, we achieved excellent Q-switching and mode-locking performance, demonstrating tunability and stability superior to existing SAs.
Novelty, Applications, and Future work
The novelty of this work lies in the innovative use of GNRs as a saturable absorber, which provides high nonlinear optical absorption, broad wavelength tunability, and enhanced photothermal stability. Unlike traditional semiconductor-based SAs, our GNR-PVA composite offers a cost-effective, flexible, and easily fabricated solution. The primary challenge was optimizing the size and concentration of GNRs to achieve the desired nonlinear absorption properties while maintaining stable laser performance. Future work will focus on refining the fabrication process and integrating this technology into compact and portable fiber laser systems.
Applications
Near-Term Applications: Biomedical imaging, eye-safe LIDAR, atmospheric gas
sensing, and industrial laser machining.
Long-Term Commercial Applications: Portable medical diagnostic tools, next-
generation optical communication systems, and advanced security and defense
applications.
Future Work
We plan to expand this research by collaborating with institutions focused on biomedical
photonics and remote sensing technologies. Future studies will explore alternative
nanomaterial-based SAs and extend the operating wavelength range. Research funding from
the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), the Canada
Foundation for Innovation (CFI) and MITACS has been instrumental in advancing this work, and
we look forward to further collaboration with academic and industrial partners.
Nanopartz' Role
Nanopartz gold nanorods played a critical role in this research by providing precisely engineered plasmonic nanoparticles with tailored optical absorption properties. The high-quality, monodisperse GNRs ensured consistent and repeatable performance of the saturable absorber, enabling stable Q-switching and mode-locking operations. This collaboration highlights the potential of Nanopartz products in advancing next-generation photonics and laser technologies.
Contact and Publication
Dr. Gautam Das is a Professor in the Department of Physics at Lakehead University in Thunder Bay, Ontario, Canada. He also serves as the Graduate Coordinator for the Physics program. Dr. Das earned his Ph.D. from the University of Waterloo, Canada, and another Ph.D. (Technology) from the University of Calcutta, India. His research primarily focuses on photonics, fiber lasers, fiber optics, sensing, and nanomaterials. He leads the Photonics Research Group at Lakehead University.
Contact Information:
- Email: gdas@lakeheadu.ca
- Phone: +1 (807) 343-8010 ext. 8828
- Office: CB 4027, Lakehead University, 955 Oliver Road, Thunder Bay, Ontario, P7B 5E1, Canada
For more details on Dr. Das's research and publications, you can visit his profile on the Lakehead University website. lakeheadu.ca
Nanopartz Products Used for this Research
The products used for this research are our Gold Nanorods.